Signing requests for key operations
Extra layer of security for actions that impact the outflow of funds from the Volt Account.
Signing requests for key operations
Why do you need to do this?
This is done to add an extra layer of security to actions that impact the outflow of funds from the Volt Account.
How do you do this using the API?
Every POST request to either the Refunds or Payouts API must be signed using a private key that only you have access to. You then send a JWT token, containing a signature of the JSON body of the request, in the header of each request.
This requirement does not apply to Fuzebox users. All Fuzebox operations that require signing use Strong Customer Authentication (SCA) instead.
Where can you test this?
The signing requirement is applied in both Sandbox and Production environments.
Integration steps
The high-level steps for integrating this are:
- Create an RSA public/private key pair
- Upload your public key to Volt via Fuzebox and receive a
kid(key identifier) - For each request, create a JWT token which is signed using your private key and includes your
kid - Send the JWT token in the
X-JWS-Signatureheader of each request
Create key pair
Technical specifications
Your key pair should use the following specifications:
- Algorithm: RSA
- Key length: 2048 bits
- Format: PEM
How to generate your keys
You can generate your keys directly in Fuzebox under Configuration > Customers > API Access > Signature Keys > Generate a new key pair.
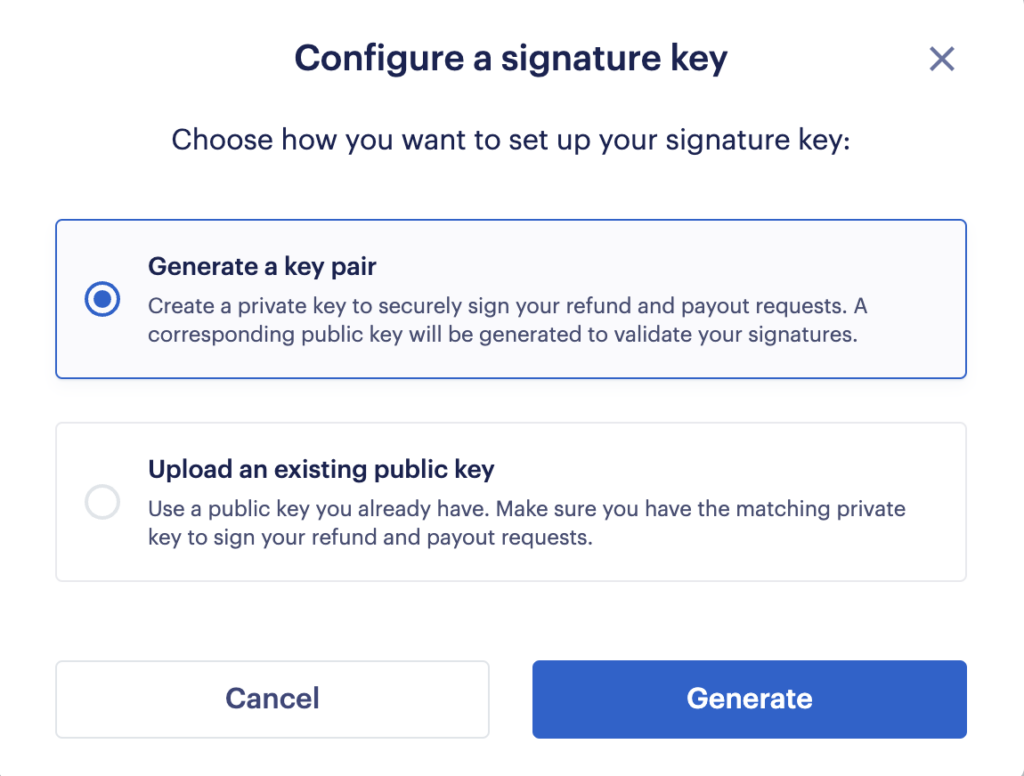
You can also generate your private / public key pair using a terminal which supports the openssl command:
openssl genrsa -out private.pem 2048
openssl rsa -in private.pem -outform PEM -pubout -out public.pemIf you generated the key pair outside of Fuzebox, please upload your public key to Fuzebox under Configuration > Customers > API Access > Signature Keys > Upload an existing public key.
Volt does not store your private key. You must store it securely on your side. If you lose your private key, you will need to generate a new key pair and upload the new public key to Fuzebox.
Create a JWT token for each request
To sign each request, you will need to provide a JWT token in the header of that request. To generate a signed JWT token, you'll need your private key and the ID of your public key (kid), plus the payload (the JSON body) of the POST request.
Creating your JWT token
A JWT token consists of three segments, separated by dots: header.payload.signature. However, for this implementation, we use a detached payload. This means the final token will look like header..signature (with two dots and no payload in the middle).
The token header segment
The header segment of the JWT should contain the following fields:
{
"alg": "RS256",
"kid": "your-key-id-from-fuzebox",
"typ": "JWT"
}Encoding the header
You then need to Base64Url encode this JSON. For example:
eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6ImY1MGY4ZTRiLTg0YjgtNDZiMS1hZGNmLTc2ZmM5YmY5YjU0MCIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9The signature segment
The signature is created by signing the header.payload string with your private key using the RS256 algorithm.
Important: You must use the exact JSON body that you are sending in your POST request as the payload for the signature. Any difference, including whitespace or field order, will result in a signature mismatch.
Build your JWT token
Once you have the signature, you concatenate the encoded header, two dots, and the encoded signature:
header..signature
Note the two dots .. in the middle. This is because we are using a detached payload.
Example of a final token:
eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6ImY1MGY4ZTRiLTg0YjgtNDZiMS1hZGNmLTc2ZmM5YmY5YjU0MCIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9..SflKxwRJSMeKKF2QT4fwpMeJf36POk6yJV_adQssw5cSign your request
Add the X-JWS-Signature header to your POST request, containing the JWT token you created.
POST /payouts HTTP/1.1
Host: api.volt.io
Authorization: Bearer your-access-token
X-JWS-Signature: eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6ImY1MGY4ZTRiLTg0YjgtNDZiMS1hZGNmLTc2ZmM5YmY5YjU0MCIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9..SflKxwRJSMeKKF2QT4fwpMeJf36POk6yJV_adQssw5c
Content-Type: application/json
{
"amount": 100,
"currency": "EUR",
...
}Simple examples of code
// Example for refunds
String jwtString = JWT.create()
.withHeader(Map.of("alg", "RS256", "kid", kid, "typ", "JWT"))
.withPayload(payload)
.sign(algorithm);
// Prepare the parsed JWT string (detached payload)
String[] parts = jwtString.split("\\.");
String parsedJwtString = parts[0] + ".." + parts[2];
// Set up the request
HttpRequest request = HttpRequest.newBuilder()
.uri(URI.create(baseUrl + "/payments/" + paymentId + "/request-refund"))
.header("Content-Type", "application/json")
.header("X-JWS-Signature", parsedJwtString)
.header("Authorization", "Bearer " + authToken)
.POST(HttpRequest.BodyPublishers.ofString(requestBody))
.build();// Example for payouts
String jwtString = JWT.create()
.withHeader(Map.of("alg", "RS256", "kid", kid, "typ", "JWT"))
.withPayload(payload)
.sign(algorithm);
// Prepare the parsed JWT string (detached payload)
String[] parts = jwtString.split("\\.");
String parsedJwtString = parts[0] + ".." + parts[2];
// Set up the request
HttpRequest request = HttpRequest.newBuilder()
.uri(URI.create(baseUrl + "/payouts"))
.header("Content-Type", "application/json")
.header("X-JWS-Signature", parsedJwtString)
.header("Authorization", "Bearer " + authToken)
.POST(HttpRequest.BodyPublishers.ofString(requestBody))
.build();How is this guide?
Last updated on